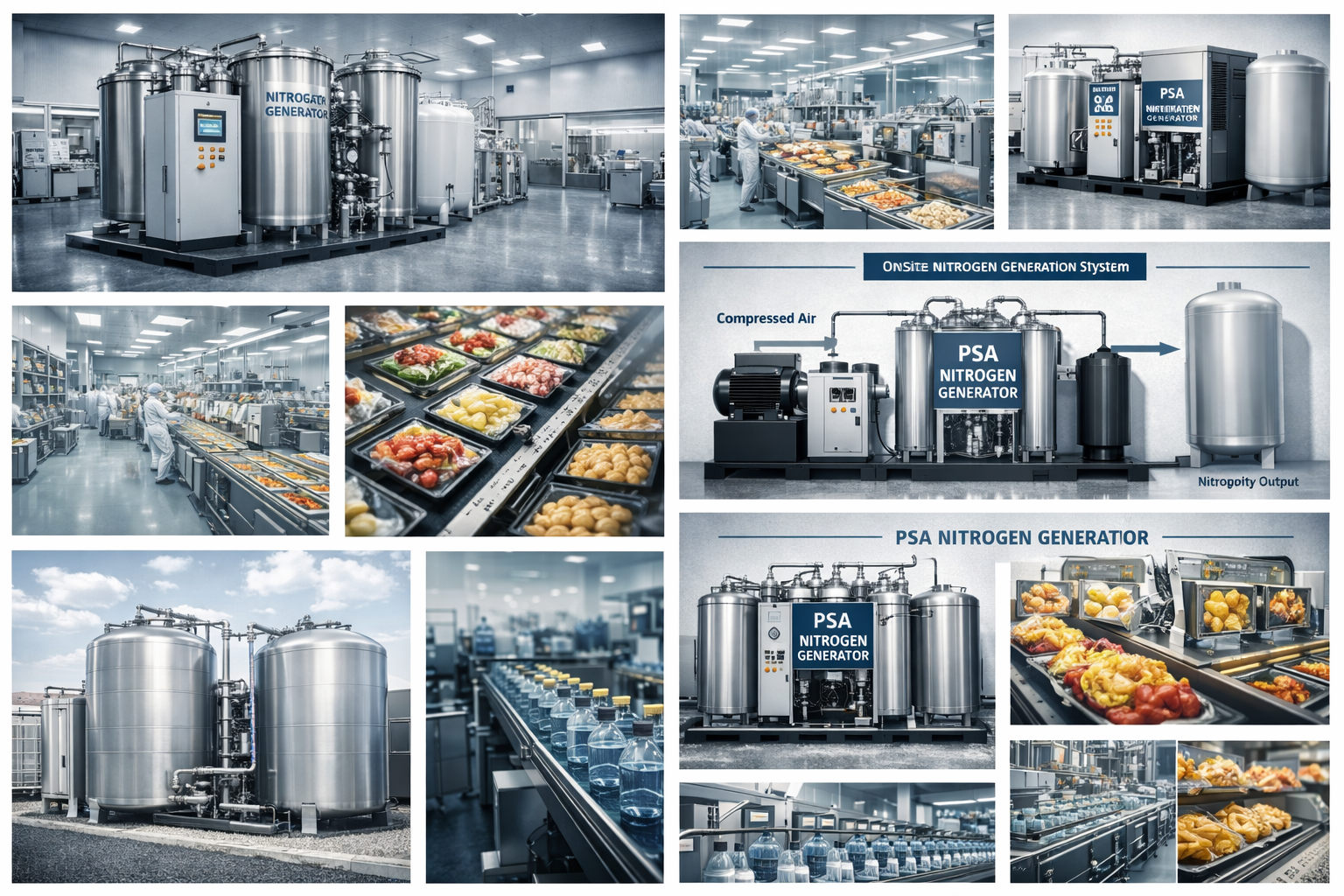
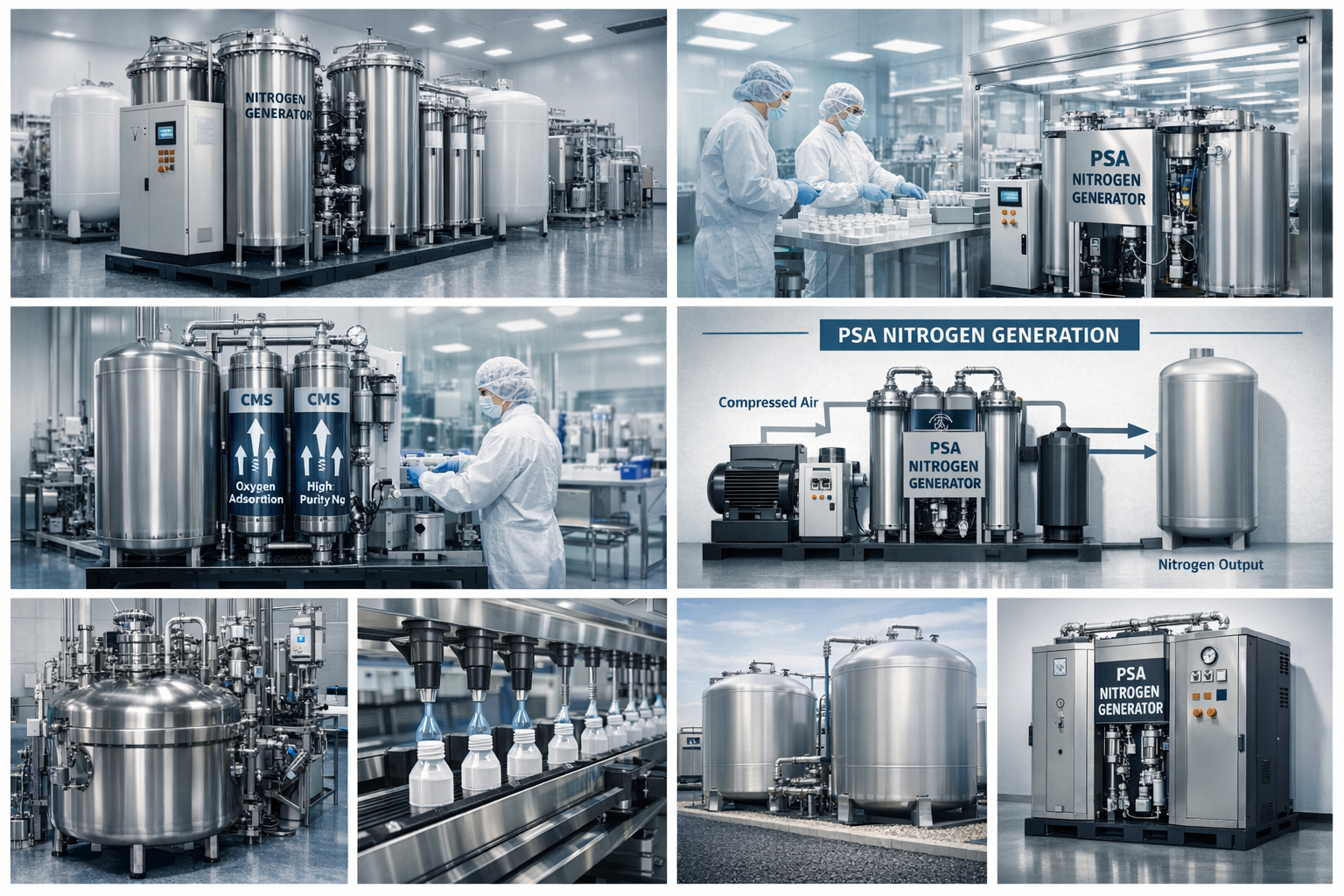
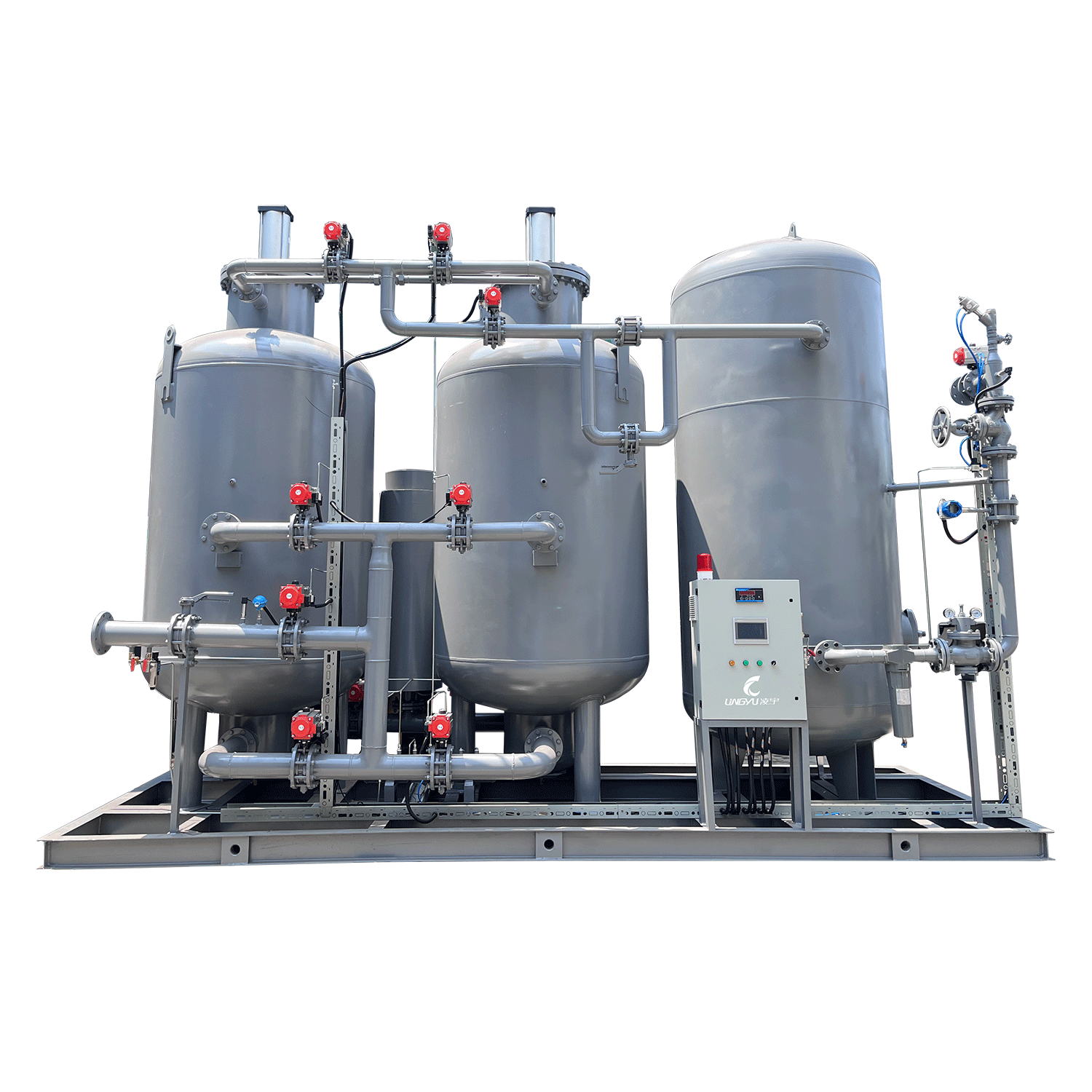
In today’s pharmaceutical and medicinal production environments, quality, purity, and safety standards are stricter than ever. One technology that plays an essential yet often overlooked role is the nitrogen generator for medicinal manufacturing. By providing a stable supply of high-purity nitrogen, these systems help ensure that medicines are produced, packaged, and stored under optimal conditions.
What Is a Nitrogen Generator?
A nitrogen generator is a system that separates nitrogen from compressed air using either Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) or membrane technology. These generators deliver nitrogen with purities ranging from 95% to 99.999%, depending on process requirements. Instead of relying on cylinders or liquid nitrogen deliveries, a generator allows pharmaceutical facilities to produce nitrogen on-site, continuously and safely.
Why Nitrogen Matters in Medicinal Manufacturing
Nitrogen is widely used across the pharmaceutical industry due to its inert, dry, and non-reactive properties. It prevents oxidation, inhibits microbial growth, and maintains controlled environments in sensitive production areas.
Key reasons nitrogen is essential include:
Preventing product degradation
Drugs such as antibiotics, vitamins, and biologics are sensitive to oxygen. Nitrogen protects them from oxidation.Creating a sterile environment
Nitrogen reduces microbial contamination and maintains cleanliness inside tanks and production lines.Improving product stability
Inerting ensures consistent quality throughout manufacturing, transport, and storage.Enhancing safety
Nitrogen displaces oxygen in processes involving flammable compounds, reducing fire and explosion risks.
Applications of Nitrogen Generators in Medicinal Manufacturing
Nitrogen generators play a role at nearly every stage of pharmaceutical production:
1. Inerting and Blanketing
During mixing, blending, and holding, nitrogen blankets the product to prevent contact with oxygen.
2. Packaging and Filling
Nitrogen is used to purge bottles, vials, blisters, and bags, ensuring a clean, dry atmosphere before filling.
3. Flushing and Pressurizing
Nitrogen flushes pipelines and storage tanks to keep moisture and contaminants out.
4. Lyophilization (Freeze-Drying)
Some freeze-drying processes require nitrogen to maintain controlled pressure and purity levels.
5. Powder Conveying
Nitrogen provides a safe, inert medium for transferring sensitive pharmaceutical powders.
6. Storage and Preservation
Nitrogen-filled environments extend shelf life, especially for oxygen-sensitive products.
Advantages of Using an On-Site Nitrogen Generator
Installing a nitrogen generator for medicinal manufacturing offers several important benefits:
1. Consistent Purity and Quality
On-site generators deliver stable nitrogen purity tailored to GMP and pharmaceutical standards.
2. Cost Efficiency
No more cylinder rentals, deliveries, or liquid nitrogen logistics—significantly reducing long-term operating costs.
3. Enhanced Safety
On-site production eliminates the risks associated with high-pressure nitrogen cylinders.
4. Continuous, Uninterrupted Supply
Production never stops, even during supply-chain disruptions.
5. Environmentally Friendly
Generating nitrogen on demand reduces carbon emissions from transportation and eliminates cylinder waste.
Choosing the Right Nitrogen Generator
When selecting a nitrogen generator for medicinal manufacturing, consider:
Required nitrogen purity
Flow rate and pressure demands
Facility size and available installation space
Compliance with pharmaceutical GMP standards
Energy consumption
Maintenance requirements
PSA vs. membrane technology
A proper assessment ensures a reliable system that meets both current and future production needs.
Final Thoughts
A nitrogen generator for medicinal manufacturing is more than just a support tool—it is a core technology that ensures safety, efficiency, and product integrity throughout the pharmaceutical production cycle. As manufacturers continue to pursue higher quality standards and tighter operational control, on-site nitrogen generation has become a strategic investment for modern medicinal facilities.