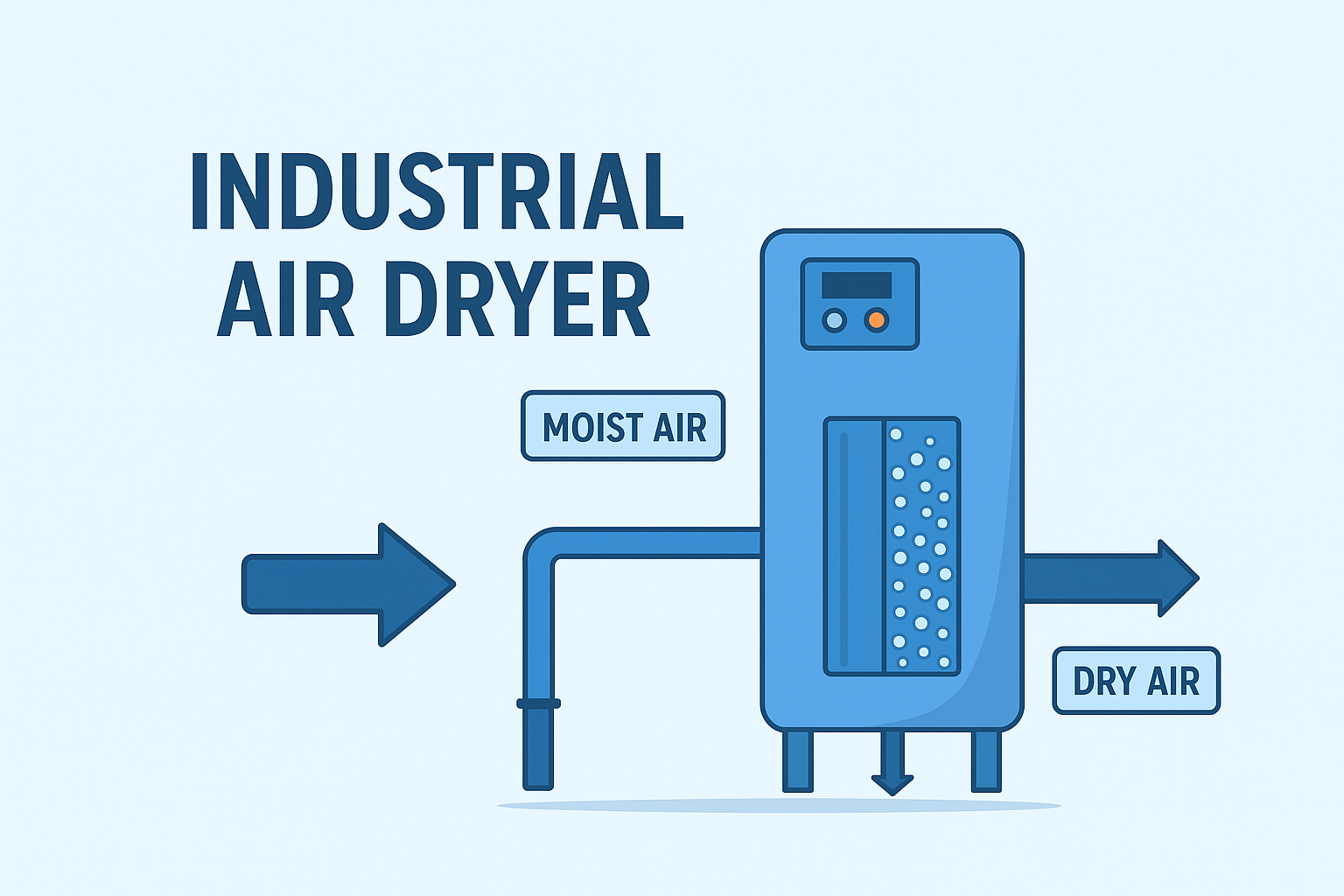
Moisture is one of the biggest challenges in industrial compressed air systems. When air is compressed, water vapor condenses into liquid, which can damage machinery, contaminate products, and reduce production efficiency. To solve this problem, manufacturers use an industrial air dryer—a system designed to remove moisture from compressed air and ensure clean, dry, and reliable air supply.
In this article, we explain what an industrial air dryer is, how it works, the main types available on the market, and where it is commonly used.
What Is an Industrial Air Dryer?
An industrial air dryer is a moisture-removal system used in factories and commercial facilities to dry compressed air before it is delivered to equipment or production lines. These dryers are built for heavy-duty operation and offer high airflow capacity, stable dew points, and long-term reliability.
Industrial air dryers prevent:
Corrosion in pipelines and air tools
Damage to machinery and pneumatic equipment
Product contamination from moisture or oil
Reduced efficiency in automation systems
Failures caused by condensation in valves and actuators
In industries where precision and cleanliness matter, dry air is essential.
How an Industrial Air Dryer Works
The drying process varies depending on the technology used, but all dryers share the same basic function: remove water vapor from compressed air before it enters the production system.
Typical stages include:
1. Moist compressed air enters the dryer
The air comes directly from an air compressor, usually warm and saturated with vapor.
2. Water is removed by cooling, absorption, or filtration
The dryer uses refrigeration, desiccant materials, or membrane separation to extract moisture.
3. Clean, dry compressed air exits the system
Dry air is then delivered to industrial equipment, preventing rust and performance issues.
4. Drain systems remove collected moisture
Automatic drain valves ensure water does not accumulate inside the dryer.
Types of Industrial Air Dryers
Different industries require different drying levels. Here are the main types:
✔ Refrigerated Air Dryer
Cools air to condense moisture
Economical and widely used
Ideal for general industrial applications
Typical dew point: 2–10°C (35–50°F)

The 3885 CFM water-cooled refrigerated air dryer is an industrial moisture-removal system designed for facilities that require stable and efficient drying performance. Suitable for large compressed air networks, it provides reliable dew point control and long-term protection for downstream equipment in demanding environments.
✔ Desiccant Air Dryer (Adsorption Dryer)
Uses moisture-absorbing materials like activated alumina
Suitable for environments requiring ultra-dry air
Works well in cold climates or sensitive processes
Dew point as low as −40°C to −70°C (−40°F to −94°F)
2., Resists chemical corrosion and extends service life
3. Special sealing technology prevents flammable gases or dust from entering theinterior of the machine
4. Regeneration gas consumption can be adjusted, with energy saving and dewpoint adjustment function
✔ Membrane Air Dryer
Uses selective membranes to remove moisture
Compact, quiet, and energy-efficient
Suitable for small to medium-scale operations

2, Rated inlet pressure: 0.7MPa (0.6MPa~1.0MPa is allowed,other pressure levelsare available for customization)
3. Rated inlet temperature: 10'C~30'C (limit inlet temperature: ≤40°C)
4. Inlet air dew point: <15°C
✔ Heatless & Heated Regeneration Dryers
Designed for large factories needing continuous high-flow dry air
Common in chemical, pharmaceutical, and power industries

Utilizes high-performance pneumatic valves;
Equipped with a fully electronic programmable controller,.
Why Industrial Air Dryers Matter
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Protects equipment | Prevents corrosion and premature wear |
| Improves product quality | Prevents moisture contamination |
| Reduces maintenance costs | Fewer failures and part replacements |
| Enhances energy efficiency | Smooth operation with less air loss |
| Ensures reliability in extreme environments | Suitable for low-temperature or high-humidity areas |
Without a proper drying system, air compressors become far less efficient and far more costly to maintain.
Where Industrial Air Dryers Are Used
Industrial air dryers serve critical roles in many fields, including:
Food & beverage manufacturing
Pharmaceutical production
CNC machining and metal processing
Automotive and aerospace industries
Chemical and petrochemical plants
Textile and plastics molding
Packaging and printing industries
Power stations and energy facilities
Any industry requiring clean, dry compressed air benefits from a dryer.
Conclusion
An industrial air dryer is a key component in any factory using compressed air. By removing moisture, it protects machinery, reduces downtime, and ensures high-quality production output. Choosing the right dryer depends on operating conditions, required dew point, air volume, and environmental factors.