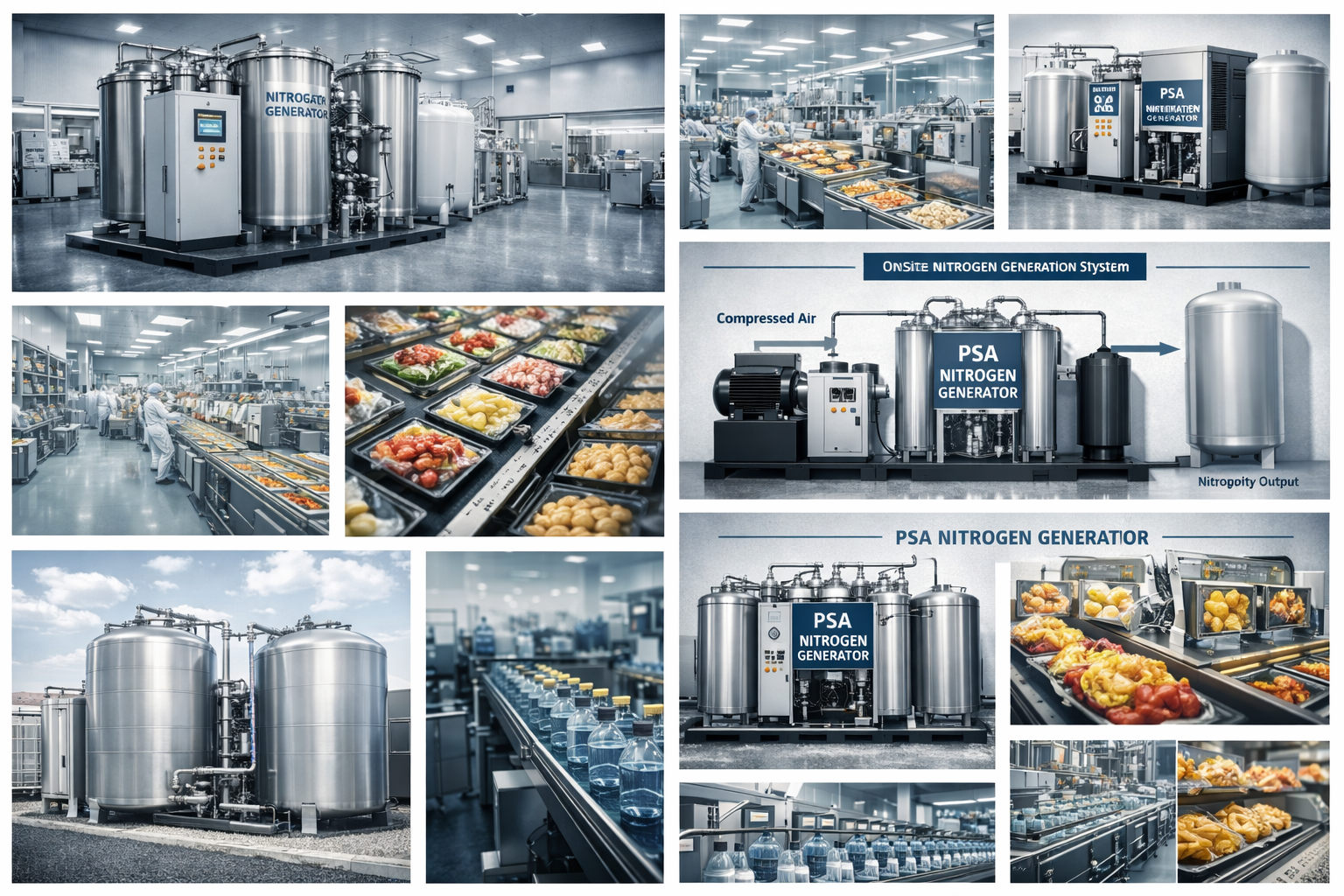
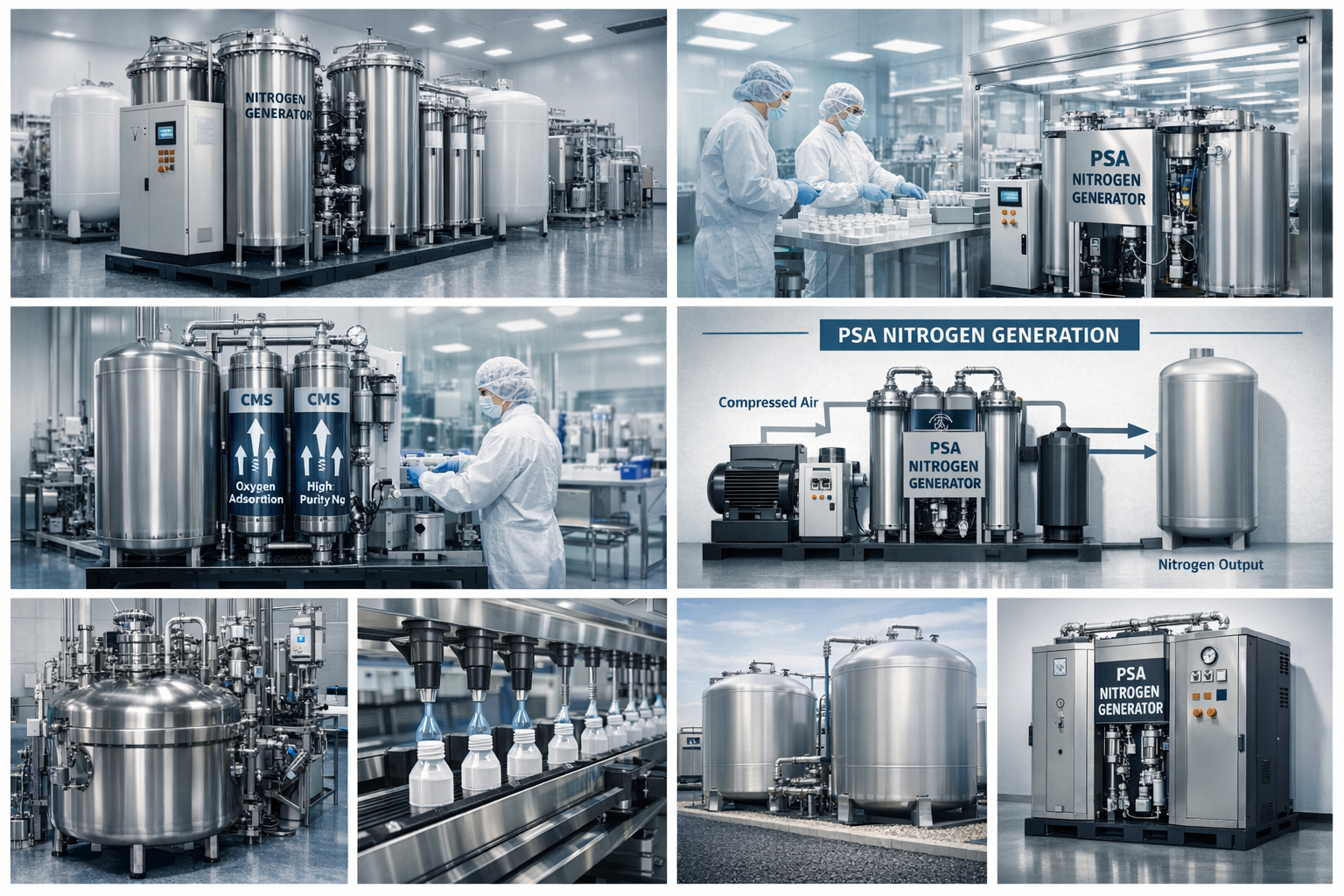
In any pneumatic system, clean and dry compressed air is essential for protecting equipment and ensuring reliable performance. Moisture, even in small amounts, can lead to corrosion, clogging, reduced efficiency, and costly downtime. That’s where a pneumatic air dryer becomes a crucial part of the system.
This article explains what a pneumatic air dryer is, how it works, its main benefits, and how to choose the best model for your application.
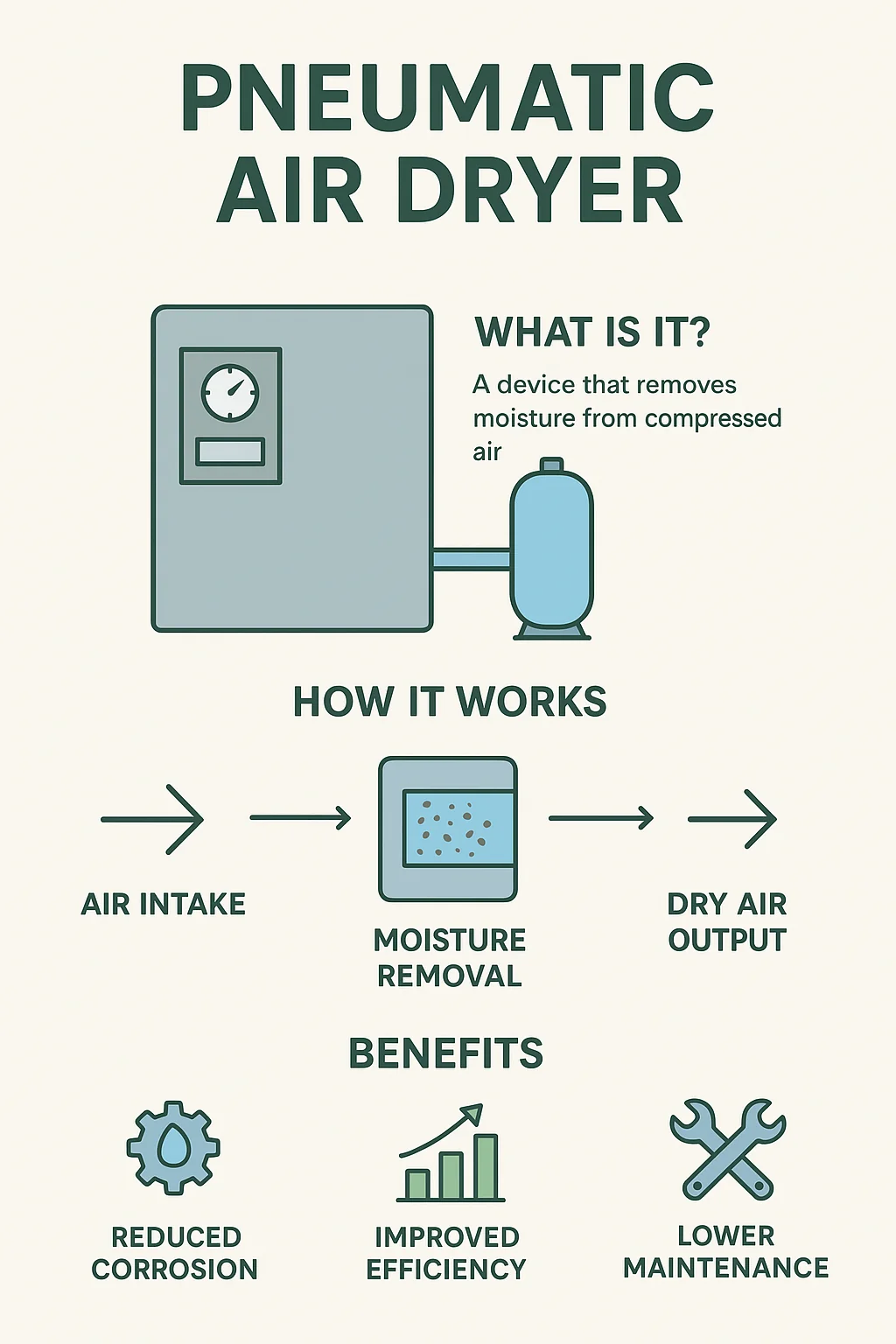
What Is a Pneumatic Air Dryer?
A pneumatic air dryer is a device designed to remove moisture from compressed air before it reaches tools, valves, actuators, and other components in a pneumatic system. By controlling humidity, pneumatic air dryers eliminate water vapor, liquid condensation, and contaminants that could otherwise damage equipment or affect production output.
These dryers are used in industries such as:
Manufacturing & automation
Automotive and aerospace
Food & beverage
Pharmaceutical production
Electronics and precision equipment
Energy and chemical processing
Why Moisture Is a Problem in Pneumatic Systems
Compressed air naturally contains water vapor. When air is compressed, its temperature rises—and once it cools inside the system, moisture condenses into liquid water. This can lead to:
Rust and corrosion of pipes and tools
Premature wear of pneumatic cylinders and valves
Freezing in cold environments
Contamination of products in sensitive industries
Reduced system efficiency
A pneumatic air dryer prevents these issues entirely by removing moisture before it enters the air distribution network.
How a Pneumatic Air Dryer Works
Although different technologies exist, most pneumatic air dryers follow a similar process:
1. Air Intake
Moist compressed air enters the dryer from the compressor.
2. Moisture Removal
Depending on the dryer type, moisture is removed by:
Cooling the air (refrigeration dryers)
Adsorption using desiccant beads (desiccant dryers)
Filtration and separation (membrane dryers)
3. Dry Air Output
Dry, clean air exits the dryer and flows to pneumatic tools and equipment.
4. Purge or Drain (if applicable)
Collected water or saturated desiccant is purged or regenerated automatically.
Common Types of Pneumatic Air Dryers
1. Refrigerated Air Dryers
Lower the air temperature to condense and remove moisture
Great for general manufacturing and shop applications

2. Desiccant Air Dryers
Use moisture-adsorbing beads
Achieve extremely low dew points
Ideal for sensitive or ultra-dry air requirements

3. Membrane Air Dryers
Use selective filtration
Compact, quiet, and maintenance-friendly
Great for remote or point-of-use installations
4. Deliquescent Air Dryers
Use dissolvable tablets that absorb moisture
Simple and low-maintenance
Each dryer type serves a unique purpose depending on humidity level and dew point requirements.
Benefits of Using a Pneumatic Air Dryer
✔ Reduced Corrosion and Equipment Damage
Dry air prevents rust and extends the life of air tools, valves, and cylinders.
✔ Improved System Efficiency
Moisture-free systems operate more smoothly, delivering consistent pressure and airflow.
✔ Lower Maintenance Costs
With less contamination and corrosion, equipment requires fewer repairs and replacements.
✔ Better Product Quality
Industries like food, pharmaceutical, and electronics rely on clean, dry air for safe and accurate production.
✔ Enhanced Reliability
Pneumatic tools and automation systems perform more predictably with stable, dry air.
How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Air Dryer
When selecting a dryer, consider:
1. Required Dew Point
How dry does your air need to be?
General use: refrigerated dryer
Critical applications: desiccant dryer
2. Flow Rate Capacity
Match dryer capacity with compressor output to avoid pressure drop.
3. Operating Environment
Hot, humid, or cold conditions may require different technologies.
4. Energy Efficiency
Dryers run continuously in many plants, so energy consumption matters.
5. Maintenance Requirements
Some dryers need periodic desiccant replacement or automatic drainage.
Conclusion
A pneumatic air dryer is not just an accessory—it is a core component of any compressed air system. By eliminating moisture, it ensures higher efficiency, longer equipment life, and consistent performance across all pneumatic operations.
Whether you run a small workshop or a large industrial plant, investing in the right air dryer will protect your equipment and improve overall productivity.