Nitrogen is one of the most abundant elements on Earth, yet many people don’t realize how deeply it has shaped science, industry, and everyday life. Whether in ancient natural cycles or advanced modern technologies, nitrogen has played a central role in human progress.
So, what was nitrogen used for historically—and how is it used today? Let’s explore its journey.
Early Understanding: Nitrogen in Nature
Long before nitrogen gas (N₂) was isolated and identified by scientists, it was already vital to life on Earth. In early civilizations, people didn’t know nitrogen by name, but they recognized the value of nitrogen-rich soil.
Early Uses (Before Industrial Chemistry)
Agriculture: Farmers used natural fertilizers—such as manure and compost—rich in nitrogen compounds to increase crop yields.
Food Preservation: Saltpeter (potassium nitrate), a natural nitrogen compound, was used for curing meats and preserving foods.
Early Medicine: Nitrogen compounds were part of herbal remedies and traditional treatments, though their chemistry was not yet understood.
These early practices demonstrated how nitrogen, even without scientific knowledge, was part of human survival.
Scientific Discovery: Nitrogen in the 18th and 19th Centuries
Nitrogen gas was first isolated in 1772 by Daniel Rutherford. Once discovered, scientists began exploring how this inert gas and its related compounds could be used.
Key Uses During This Period
Gunpowder Production: Nitrate compounds became essential for weapons, mining, and construction.
Chemical Research: Nitrogen helped researchers understand gases, combustion, and atmospheric science.
Metal Treatment: Ammonia and nitrides were used in early metallurgical experiments.
This era laid the groundwork for today’s industrial nitrogen applications.
20th Century Innovation: Nitrogen Becomes Industrial
The invention of the Haber-Bosch process in the early 1900s changed everything. This technology allowed industries to convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia—a breakthrough that transformed global agriculture and manufacturing.
Major 20th Century Applications
1. Fertilizer Production
Nitrogen-based fertilizers dramatically boosted global food production. They remain essential for feeding the world’s population.
2. Explosives and Propellants
Nitrogen compounds were crucial for:
TNT
Ammonium nitrate explosives
Rocket fuels
3. Refrigeration and Cooling
Liquid nitrogen began being used for:
Cryogenic freezing
Medical storage
Industrial cooling
Scientific experiments
4. Welding and Metal Processing
Nitrogen became a shielding gas to protect metal from oxidation.
5. Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals
Nitrogen supported the production of medicines, plastics, and synthetic fibers.
Nitrogen was no longer just an atmospheric gas—it became an industrial powerhouse.
Modern Uses: Nitrogen in Today’s World
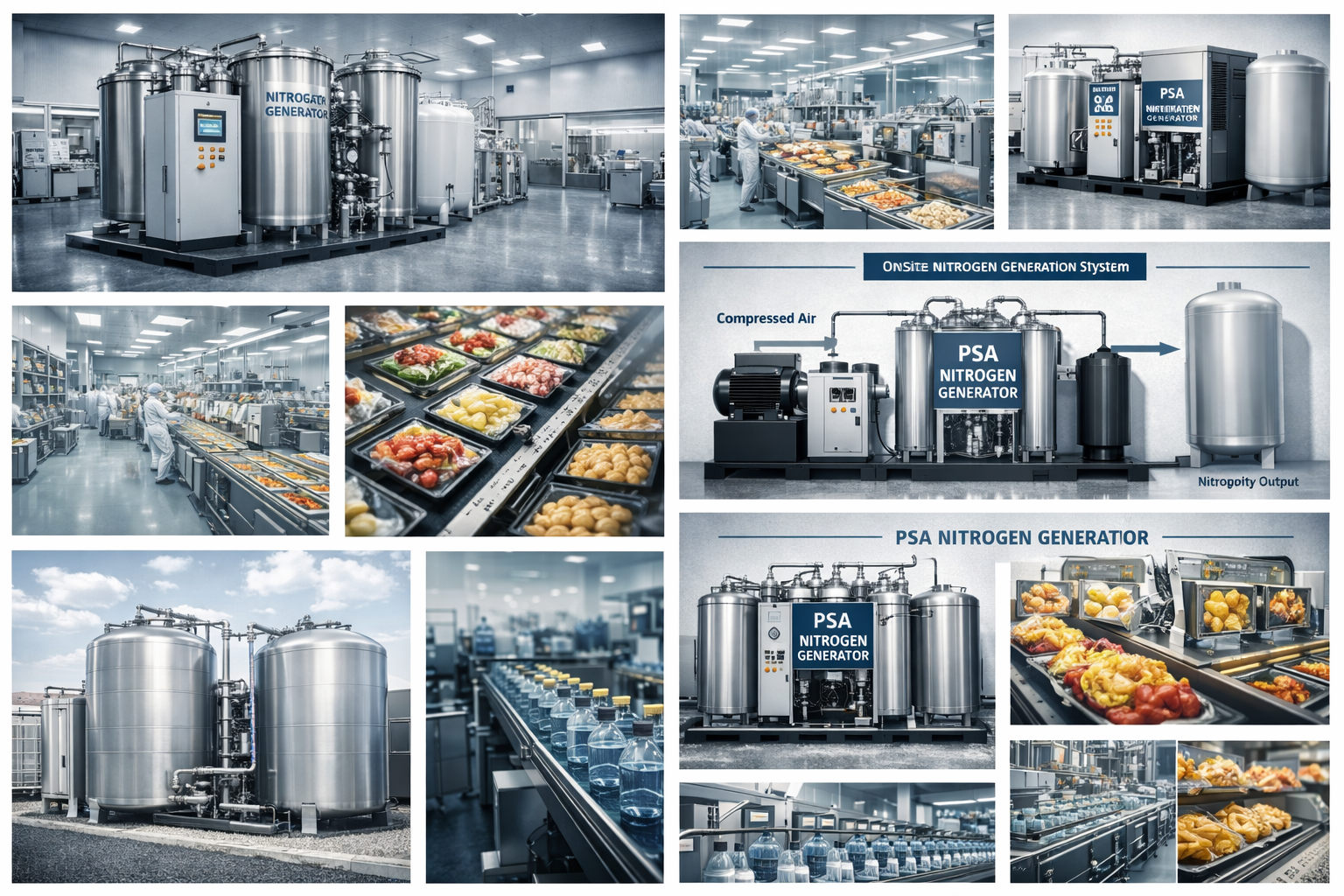
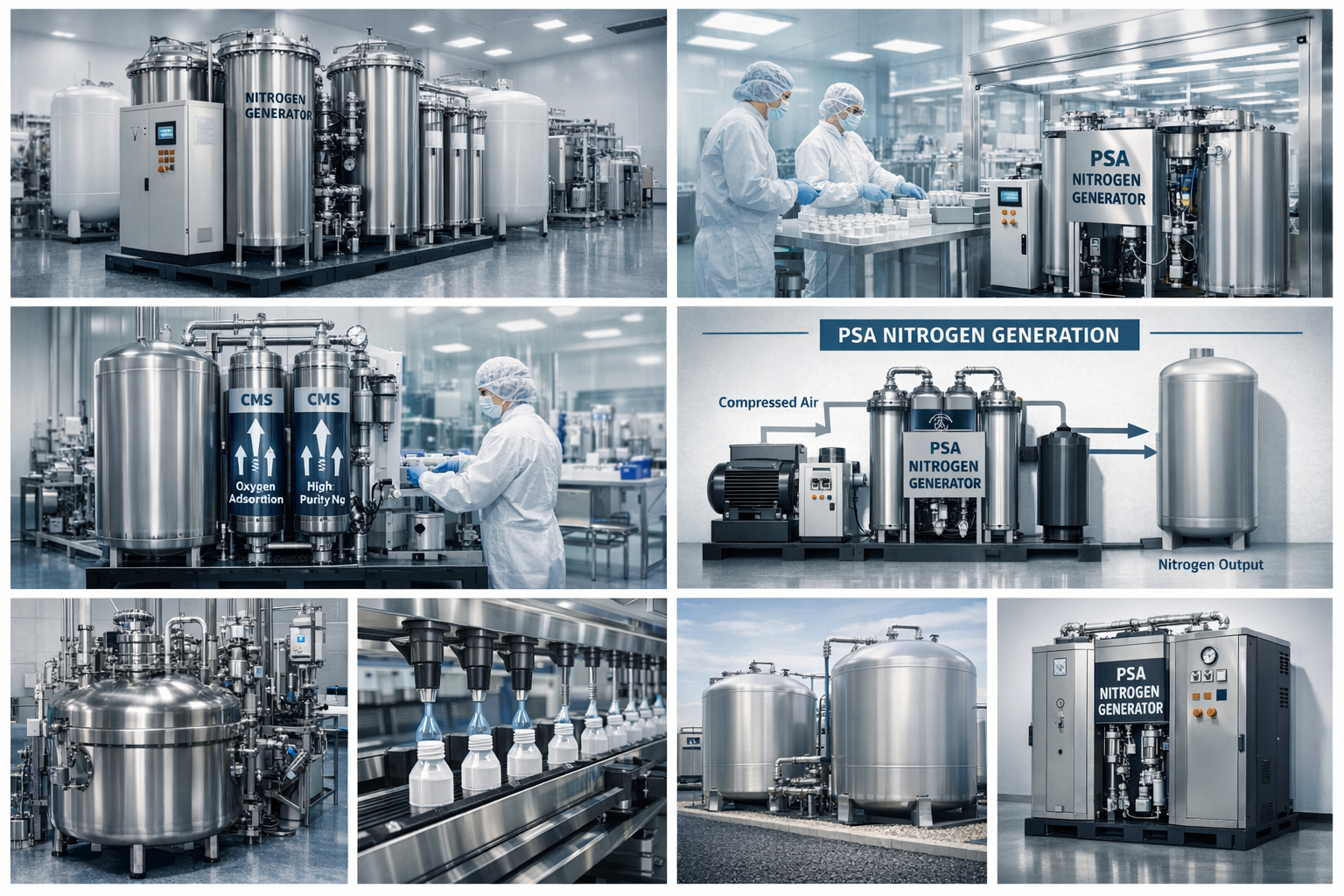
Today, nitrogen is used in almost every major industry. Its stability, non-flammability, and high purity make it essential for both safety and performance. With the increasing demand for on-site nitrogen supply, many facilities now rely on a Nitrogen Generator to produce stable, cost-efficient nitrogen for daily operations.
Modern Applications Include:
1. Electronics Manufacturing
Nitrogen creates clean, controlled environments for producing semiconductors and circuit boards. Many electronics factories use a Nitrogen Generator to ensure a continuous supply of high-purity nitrogen without depending on bulk deliveries.
2. Food and Beverage Packaging
Nitrogen flushes oxygen out of packaging to:
Prevent oxidation
Maintain freshness
Extend shelf life
This is why chips remain crunchy inside sealed bags. Food companies increasingly choose on-site Nitrogen Generators to maintain consistent nitrogen purity and reduce long-term packaging costs.
3. Medical Technology
Nitrogen supports:
Cryosurgery
Storage of biological samples
Medical gas mixtures
Hospitals and laboratories often use Nitrogen Generators for reliable, medical-grade nitrogen production.
4. Automotive and Aerospace
Nitrogen is used for:
Tire inflation
Inerting fuel tanks
Preventing fire risks
High-pressure testing
A Nitrogen Generator provides a safe and uninterrupted supply for these critical applications.
5. Laboratory and Scientific Research
From liquid nitrogen cooling to creating inert atmospheres for experiments, nitrogen is foundational to modern science. Many research facilities integrate Nitrogen Generators to achieve precise, on-demand nitrogen flow for sensitive experiments.
Conclusion: Nitrogen’s Past, Present, and Future
From ancient soil fertility to advanced semiconductor production, nitrogen has evolved from a misunderstood atmospheric gas into one of the most important industrial resources on Earth.
Historically, nitrogen was used in agriculture, food preservation, and early chemistry.
Today, it is essential in manufacturing, medicine, food packaging, electronics, and cryogenics.
Nitrogen’s journey reflects humanity’s progress—and its role will only grow as technology advances.