When operating a compressed air system, moisture is one of the biggest threats to performance and equipment longevity. That’s where refrigerated air dryers come in. But how does a refrigerated air dryer work exactly? This guide breaks it down with technical clarity and practical insights, helping you understand the process and make better decisions for your compressed air system.
Whether you’re managing a workshop, manufacturing facility, or automated assembly line, this guide will explain in detail how a refrigerated air dryer works, why it’s essential, and how to choose and maintain the right one for your operation.
🧊 What Is a Refrigerated Air Dryer?
A refrigerated air dryer is a type of compressed air treatment system designed to remove water vapor from compressed air. Moisture in compressed air leads to corrosion, equipment failure, contamination, and reduced efficiency. By cooling the compressed air, refrigerated dryers cause the moisture to condense into water droplets, which are then removed through a drainage system.
Now let’s answer the key question: how does a refrigerated air dryer work?
⚙️ How Does a Refrigerated Air Dryer Work?
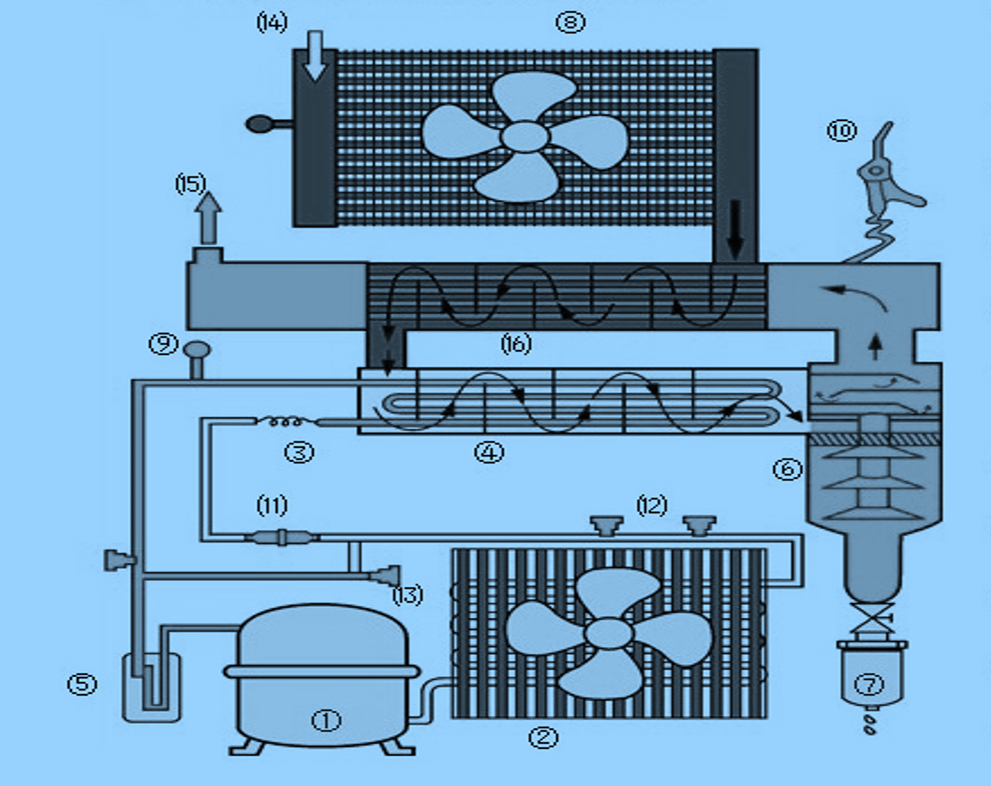
The process by which a refrigerated air dryer works can be broken down into several core stages:
🔹 Step 1: Hot, Moist Compressed Air Enters the Dryer
Compressed air leaving the compressor contains significant amounts of water vapor and heat. This air enters the dryer at elevated temperatures and high pressure.
🔹 Step 2: Pre-Cooling (Optional in High-Efficiency Models)
Some systems include a pre-cooler that exchanges heat between outgoing cool dry air and the incoming hot wet air, improving energy efficiency.
🔹 Step 3: Refrigeration Cooling Process
The compressed air is cooled down by a refrigeration system (similar to a household refrigerator). The temperature is reduced to approximately 35°F to 50°F (1.6°C to 10°C).
🔹 Step 4: Moisture Condensation
At these temperatures, the water vapor condenses into liquid water. The lower the air temperature, the more moisture condenses.
🔹 Step 5: Moisture Separation
The condensed water is separated using a moisture separator (usually a centrifugal or coalescing type) and discharged via an automatic condensate drain.
🔹 Step 6: Reheating (in some models)
To prevent condensation in downstream pipes, the cooled and dried air is reheated by the incoming warm air in a heat exchanger before leaving the system.
🧩 Key Components in a Refrigerated Air Dryer
To understand how does a refrigerated air dryer work, it’s important to know the components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Compressor (internal) | Circulates refrigerant inside the dryer system |
| Condenser | Removes heat from refrigerant to liquefy it |
| Evaporator | Cools the compressed air, causing moisture to condense |
| Moisture Separator | Physically separates water droplets from the air |
| Automatic Drain Valve | Discharges condensed water automatically |
| Heat Exchanger (optional) | Transfers heat between outgoing and incoming air for energy savings |
🌟 Benefits of Refrigerated Air Dryers
Now that we’ve explained how a refrigerated air dryer works, here are the practical advantages of using one:
✅ Reduces corrosion and rust in pipelines and tools
✅ Protects sensitive equipment like CNC machines and pneumatic tools
✅ Improves product quality in painting, packaging, and food processing
✅ Minimizes downtime and maintenance costs
✅ Ensures ISO 8573 air quality compliance
🔬 Types of Refrigerated Air Dryers
There are two main types, both of which share the same core operating principle.
1. Non-Cycling Refrigerated Air Dryer
Keeps the refrigeration circuit running continuously
Suitable for consistent air flow environments
Less energy efficient but simple in design
2. Cycling Refrigerated Air Dryer
Uses thermal mass or variable speed technology
Turns off the refrigeration compressor when not needed
More energy efficient and ideal for fluctuating demands
🛠️ How to Choose the Right Refrigerated Air Dryer
When asking how does a refrigerated air dryer work, you should also ask how to choose the right one. Consider the following:
Air Flow Rate (CFM) – Match your dryer to your compressor’s flow capacity.
Inlet Air Temperature – Standard dryers handle up to 100°F; high-temp models go higher.
Ambient Temperature – Ensure your dryer can perform in your facility’s temperature range.
Required Dew Point – Most refrigerated dryers offer a dew point of ~38°F; for lower, use desiccant dryers.
Compressor Type – Rotary screw compressors pair well with refrigerated dryers.
💡 Common Applications
Automotive repair shops
Electronics manufacturing
Metal fabrication
Food and beverage packaging
Textile and paper industries
General industrial air systems
❓ FAQ – How Does a Refrigerated Air Dryer Work?
Q1: Is a refrigerated air dryer suitable for all industries?
A: Most general industrial applications benefit from refrigerated dryers. However, processes requiring ultra-dry air (e.g., pharmaceuticals) may require desiccant dryers.
Q2: What dew point can I expect from a refrigerated air dryer?
A: Typically around 35–50°F (1.6–10°C). For lower dew points, consider desiccant air dryers.
Q3: Do refrigerated dryers remove oil too?
A: No. You’ll need coalescing filters before or after the dryer to remove oil aerosols and particles.
Q4: Can I install the dryer outdoors?
A: Only if the dryer is rated for outdoor use. Otherwise, place it in a well-ventilated indoor space.
Q5: How often should I perform maintenance?
A: Check filters monthly, clean condensers quarterly, and service refrigerants annually.
📌 Final Thoughts
Understanding how does a refrigerated air dryer work is key to maintaining a high-performance compressed air system. By removing moisture from compressed air, these dryers protect tools, reduce downtime, and improve efficiency across various industries.
With multiple designs, capacities, and configurations, there’s a refrigerated air dryer for nearly every application. Choosing the right one—and maintaining it properly—ensures long-lasting performance and energy savings.
If you’re planning to upgrade or install a refrigerated air dryer, make sure to assess your air demand, temperature conditions, and dew point requirements. With the right setup, your system will deliver dry, clean air reliably—day after day.
Related products:

The 3885 CFM refrigerated air dryer (water cooled) is a high-capacity industrial solution designed for removing moisture from large-scale compressed air systems. Built for continuous and demanding operation, this water-cooled unit ensures a steady dew point and maximum system protection. Whether you're operating in petrochemical, steel, manufacturing, or pharmaceutical industries, the 3885 CFM refrigerated air dryer delivers superior drying performance and energy efficiency.

The 4238 CFM refrigerated air dryer (water cooled) is a high-capacity, industrial-grade dryer designed to eliminate moisture from large compressed air systems. Built with a powerful water-cooled refrigeration circuit, this dryer ensures reliable and continuous moisture removal with a stable pressure dew point. For industries that demand high airflow rates and dependable air quality, the 4238 CFM refrigerated air dryer (water cooled) is the ideal solution.

The 8830 CFM refrigerated air dryer (water cooled) is a top-tier industrial solution engineered to remove moisture from large-scale compressed air systems. Built for ultra-high capacity applications, this dryer ensures consistently dry air with a stable dew point and superior thermal control using an advanced water-cooled condenser system.